A study conducted by the World Economic Forum and Boston Consulting Group showed that 72% of about 1000 surveyed managers are considering data sharing to improve operating procedures. The following cases provide examples where the exchange of data between companies would be sensible to make operating processes more efficient.
Improving plant utilization: By combining data from multiple users of the same machine type, manufacturers can improve algorithms, for example to enable predictive maintenance. Therefore, the shared use of data can optimize plant performance by increasing machine uptime and improving product quality, resulting in a win-win situation for all participants. This is particularly important for manufacturers that lack the data volume required for robust analysis algorithms.
Tracking products along the value chain: End-to-end transparency of their value chains allows manufacturers to proactively minimize risks, respond to unexpected events quickly and reduce their inventories. Although manufacturers already track products along the supply chain, they need to work together, use data jointly and deploy shared systems in order to establish true end-to-end transparency and mutually beneficial cooperation.
Decentralized real-time control through the analysis of operating data on digital platforms: The exchange of data between companies along their value chain makes it possible to establish shared digital ecosystems which enable efficient and demand-driven control of value creation.
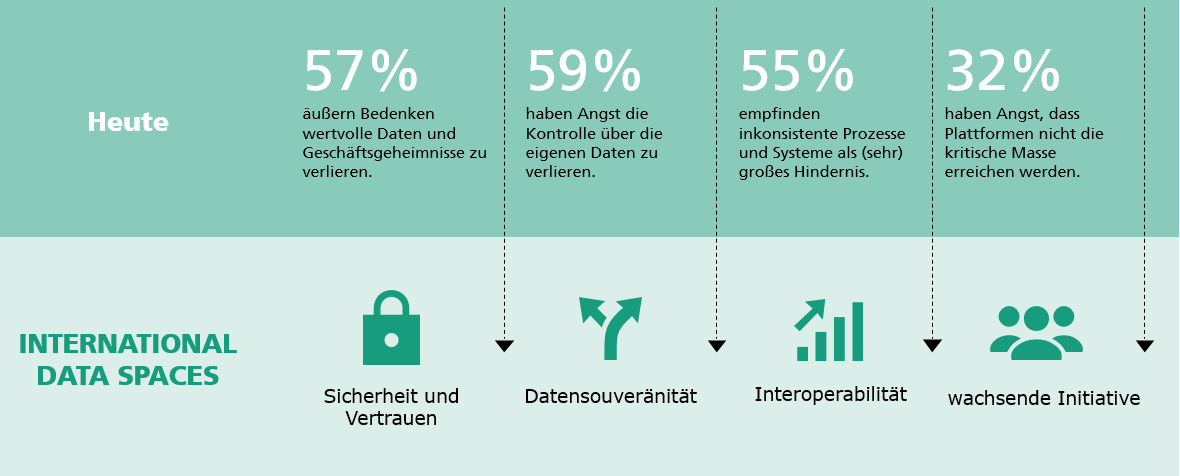
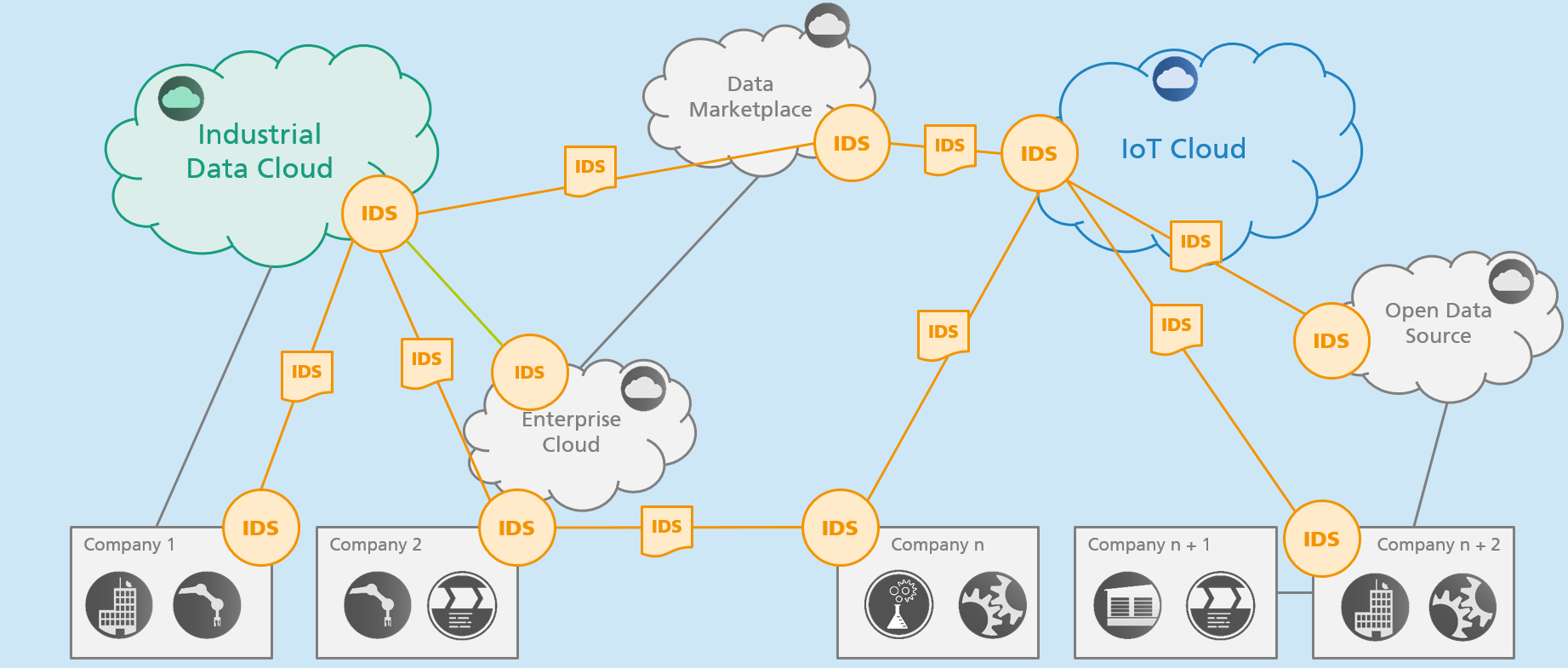
Even though the added value of these application scenarios is generally known, the exchange of data between companies frequently does not take place. The International Data Spaces architecture can enable the realization of these scenarios because it is based on generally accepted data governance models and thereby facilitates the secure exchange and straightforward linking of data within business ecosystems.
 International Data Spaces
International Data Spaces